[ad_1]
In Could 2023, the Dallas Metropolis Authorities was massively disrupted by a ransomware assault. Ransomware assaults are so-called as a result of the hackers behind them encrypt important knowledge and demand a ransom as a way to get the data decrypted.
The assault in Dallas put a halt to hearings, trials and jury responsibility, and the eventual closure of the Dallas Municipal Court docket Constructing. It additionally had an oblique impact on wider police actions, with stretched assets affecting the power to ship, for instance, summer time youth programmes. The criminals threatened to publish delicate knowledge, together with private info, court docket circumstances, prisoner identities and authorities paperwork.
One may think an assault on a metropolis authorities and police power inflicting widespread and prolonged disruption can be headline information. However ransomware assaults at the moment are so widespread and routine that the majority cross with barely a ripple of consideration. One notable exception occurred in Could and June 2023 when hackers exploited a vulnerability within the Moveit file switch app which led to knowledge theft from a whole bunch of organisations all over the world. That assault grabbed headlines, maybe due to the excessive profile victims, reported to incorporate British Airways, the BBC and the chemist chain Boots.
In response to one latest survey, ransomware funds have almost doubled to US$1.5 million (£1.2 million) over the previous yr, with the highest-earning organisations the most definitely to pay attackers. Sophos, a British cybersecurity agency, discovered that the common ransomware cost rose from US$812,000 the earlier yr. The common cost by UK organisations in 2023 was even greater than the worldwide common, at US$2.1 million.
In the meantime, in 2022 The Nationwide Cyber Safety Centre(NCSC) issued new steerage urging organisations to bolster their defences amid fears of extra state-sponsored cyber assaults linked to the battle in Ukraine. It follows a collection of cyber assaults in Ukraine that are suspected to have concerned Russia, which Moscow denies.

This text is a part of Dialog Insights
The Insights crew generates long-form journalism derived from interdisciplinary analysis. The crew is working with teachers from completely different backgrounds who’ve been engaged in initiatives aimed toward tackling societal and scientific challenges.
In actuality, not every week goes by with out assaults affecting governments, faculties, hospitals, companies and charities, everywhere in the world. These assaults have important monetary and societal prices. They will have an effect on small companies, in addition to enormous companies, and will be significantly devastating for these concerned.
Ransomware is now broadly acknowledged as a serious menace and problem to trendy society.
But ten years in the past it was nothing greater than a theoretical risk and area of interest menace. The way in which through which it has shortly developed, fuelling criminality and inflicting untold injury ought to be of main concern. The ransomware “enterprise mannequin” has turn out to be more and more subtle with, as an example, advances in malware assault vectors, negotiation methods and the construction of felony enterprise itself.
There may be each expectation that criminals will proceed to adapt their methods and trigger widespread injury for a few years to return. That’s why it’s vital that we research the ransomware menace and preempt these techniques in order to mitigate the long-term menace – and that’s precisely what our analysis crew is doing.
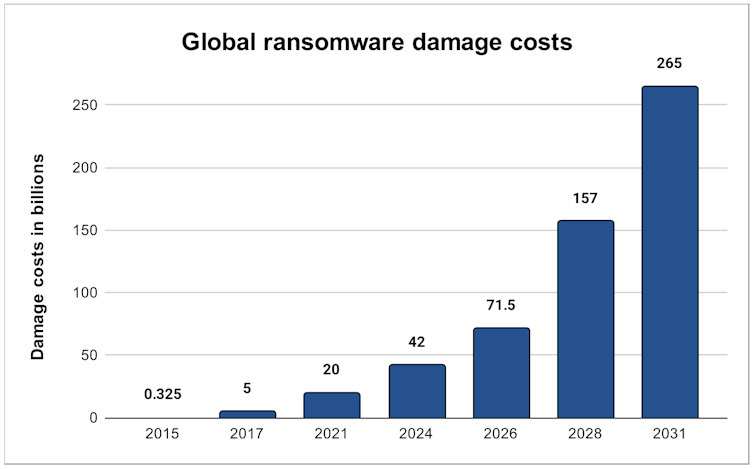
Alpesh Bhudia, CC BY-ND
Prediction of world ransomware injury prices – supply: Cyber Safety Ventures
For a few years our analysis has seemed to preempt this evolving menace by exploring new methods that ransomware criminals can use to extort victims. The goal is to forewarn, and be forward of the sport, with out figuring out specifics that may very well be utilized by criminals. In our newest analysis, which has been peer reviewed and might be printed as a part of the Worldwide Convention on Availability, Reliability and Safety (ARES), we’ve recognized a novel menace that exploits vulnerabilities in cryptocurrencies.
What’s ransomware?
Ransomware can imply subtly various things in several contexts. In 1996, Adam Younger and Mordechai “Moti” Yung at Columbia College described the fundamental type of a ransomware assault as follows:
Criminals breach the cybersecurity defences of the sufferer (both via techniques like phishing emails or utilizing an insider/rogue worker). As soon as the criminals have breached the sufferer’s defences they deploy the ransomware. The principle perform of which is to encrypt the sufferer’s information with a personal key (which will be considered an extended string of characters) to lock the sufferer out of their information. The third stage of an assault now begins with the felony demanding a ransom for the non-public key.
The straightforward actuality is that many victims pay the ransom, with ransoms doubtlessly into the thousands and thousands of {dollars}.
Utilizing this fundamental characterisation of ransomware it’s potential to differentiate several types of assault. At one excessive we there are the “low degree” assaults the place information should not encrypted or criminals don’t try and extract ransoms. However on the different excessive attackers make appreciable efforts to maximise disruption and extract a ransom.
The WannaCry ransomware assault in Could 2017 is such an instance. The assault, linked to the North Korean authorities, made no actual try and extract ransoms from victims. However, it led to widespread disruption internationally, together with to the UK’s NHS, with some cybersecurity risk-modelling organisations even saying the worldwide financial losses going into the billions.
It’s tough to discern motive on this case, however, usually talking, political intent, or easy error on the a part of the attackers might contribute to the shortage of coherent value-extraction via extortion.
Our analysis focuses on the second excessive of ransomware assaults through which criminals look to coerce cash from their victims. This doesn’t preclude a political motive. Certainly, there’s proof of hyperlinks between main ransomware teams and the Russian state. We will distinguish the diploma to which ransomware assaults are motivated by monetary achieve by observing the hassle invested in negotiation, a willingness to help or facilitate cost of the ransom, and the presence of cash laundering providers. By investing in instruments and providers which facilitate cost of the ransom, and its conversion to fiat foreign money, the attackers sign their monetary motives.
The affect of assaults
Because the assault on the Dallas Metropolis Authorities reveals, the monetary and social impacts of ransomware assaults will be numerous and extreme.
Excessive-impact ransomware assaults, such because the one which focused Colonial Oil in Could 2021 and took a serious US gas pipeline offline, are clearly harmful to the continuity of important providers.
In January 2023, there was a ransomware assault on the Royal Mail within the UK that led to the suspension of worldwide deliveries. It took over a month for service ranges to get again to regular. This assault would have had a major direct affect on the Royal Mail’s income and status. However, maybe extra importantly, it impacted all of the small companies and individuals who depend on it.
In Could 2021, the Irish NHS was hit by a ransomware assault. This affected each facet of affected person care with widespread cancellation of appointments. The Taoiseach Micheál Martin mentioned: “It’s a surprising assault on a well being service, however essentially on the sufferers and the Irish public.” Delicate knowledge was additionally reportedly leaked. The monetary affect of the assault may very well be as excessive as 100 million euros. This, nevertheless, doesn’t account for the well being and psychological affect on sufferers and medics affected by the disruption.
In addition to well being providers, training has additionally been a major goal. For example, in January 2023 a college in Guilford, UK, suffered an assault with the criminals threatening to publish delicate knowledge together with safeguarding stories and details about susceptible kids.
Assaults are additionally timed to maximise disruption. For example, an assault in June 2023 on a college in Dorchester, UK, left the varsity unable to make use of electronic mail or entry providers throughout the principle examination interval. This may have a profound affect on kids’s wellbeing and academic achievement.
These examples are certainly not exhaustive. Many assaults, as an example, instantly goal companies and charities which might be too small to draw consideration. The affect on a small enterprise, when it comes to enterprise disruption, misplaced status and the psychological value of going through the implications of an assault will be devastating. For instance, a survey in 2021 discovered that 34% of UK companies that suffered a ransomware assault subsequently closed down. And, most of the companies that continued operation nonetheless needed to lay off employees.
It started with floppy disks
The origins of ransomware are often traced again to the AIDS or PC Cyborg Trojan virus within the Eighties. On this case, victims who inserted a floppy disk of their laptop would discover their information subsequently encrypted and a cost requested. Disks have been distributed to attendees and folks occupied with particular conferences, who would then try and entry the disk to finish a survey – as a substitute turning into contaminated with the trojan. Recordsdata on affected computer systems have been encrypted utilizing a key saved domestically on every goal machine. A sufferer might, in precept, have restored entry to their information by utilizing this key. The sufferer, although, might not have recognized that they might do that, as even now, technical information of cryptography just isn’t widespread amongst most PC customers.
Ultimately, regulation enforcement traced the floppy disks to a Harvard-taught evolutionary biologist named Joseph Popp, who was conducting AIDS analysis on the time. He was arrested and charged with a number of counts of blackmail, and has been credited by some with being the inventor of ransomware. Nobody is aware of precisely what provoked Popp to do what he did.
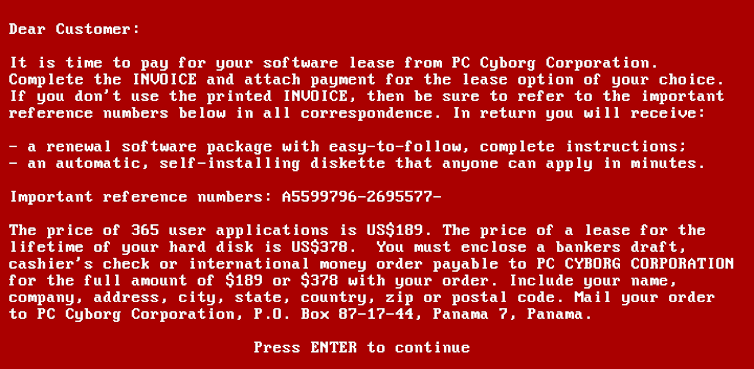
wikipedia
Many early variations of ransomware have been fairly fundamental cryptographic techniques which suffered from varied points surrounding how straightforward it was to seek out the important thing info the felony was attempting to cover from the sufferer. That is one cause why ransomware actually got here of age with the CryptoLocker assault in 2013 and 2014.
CryptoLocker was the primary technically sound ransomware assault virus to be distributed en masse. 1000’s of victims noticed their information encrypted by ransomware that might not be reverse engineered. The non-public keys, utilized in encryption, have been held by the attacker and victims couldn’t restore entry to their information with out them. Ransoms of round US$300-600 have been demanded and it’s estimated the criminals received away with round US$3 million. Cryptolocker was ultimately shut down in 2014 following an operation involving a number of, worldwide regulation enforcement companies.
CryptoLocker was pivotal in displaying proof of idea that criminals might earn massive quantities of cash from ransomware. Subsequently, there was an explosion of latest variants and new varieties. There was additionally important evolution within the methods utilized by criminals.
Off-the-shelf and double extortion
One essential growth was the emergence of ransomware-as-a-service. This can be a time period for markets on the darkish net via which criminals can receive and use “off-the-shelf” ransomware with out the necessity for superior computing expertise whereas the ransomware suppliers take a reduce of the earnings.
Analysis has proven how the darkish net is the “unregulated Wild West of the web” and a secure haven for criminals to speak and alternate of unlawful items and providers. It’s simply accessible and with the assistance of anonymisation expertise and digital currencies, there’s a world black economic system thriving there. An estimated US$1 billion was spent there through the first 9 months of 2019 alone, in accordance with the European Union Company for Legislation Enforcement.
With ransomware as a service (Raas) the barrier to entry for aspiring cyber criminals, when it comes to each value and ability, was lowered.
Underneath the Raas mannequin, experience is offered by distributors who develop the malware whereas the attackers themselves could also be comparatively unskilled. This additionally has the impact of compartmentalising danger – the arrest of cyber criminals utilizing ransomware not threatens all the provide chain, permitting assaults launched by different teams to proceed.
We’ve got additionally seen a motion away from mass phishing assaults, like CryptoLocker, which reached greater than 250,000 techniques, to extra focused assaults. That has meant an growing deal with organisations with the income to pay massive ransoms. Multinational organisations, authorized companies, faculties, universities, hospitals and healthcare suppliers have all turn out to be prime targets, in addition to many small and micro companies and charities.
A newer growth in ransomware, akin to Netwalker, REvil/Sodinokibi, has been the specter of double extortion. That is the place the criminals not solely encrypt information but additionally exfiltrate knowledge by copying the information. They then have the potential to leak or put up doubtlessly delicate and essential info.
An instance of this occurred in 2020, when one of many largest software program firms, Software program AG, was hit with a double extortion ransomware referred to as Clop. It was reported that the attackers had requested an exceptionally excessive ransom cost of US$20 million (about £15.7 million) which Software program AG refused to pay. This led to attackers releasing confidential firm knowledge on the darkish net. This gives criminals with two sources of leverage: they’ll ransom for the non-public key to decrypt information they usually can ransom to cease publication of delicate knowledge.
Double extortion modifications the enterprise mannequin of ransomware in attention-grabbing methods. Particularly, with normal ransomware, there’s a comparatively simple incentive for a sufferer to pay a ransom for entry to the non-public key if that might permit decryption of the information, they usually can not entry the information via some other means. The sufferer “solely” must belief the cyber felony will give them the important thing and that the important thing will work.
‘Honour’ amongst thieves?
However with knowledge exfiltration, against this, it’s not apparent what the sufferer will get in return for paying the ransom. The criminals nonetheless have the delicate knowledge and will nonetheless publish it any time they need. They might, certainly, ask for subsequent ransoms to not publish the information.
Subsequently, for knowledge exfiltration to be a viable enterprise technique the criminals have to construct a reputable status of “honouring” ransom funds. This has arguably led to a normalised ransomware ecosystem.
For example, ransom negotiators are non-public contractors and in some circumstances are required as a part of a cyber insurance coverage settlement to supply experience within the managing of disaster conditions involving ransomware. The place instructed, they’ll facilitate negotiated ransom funds. Inside this ecosystem, some ransomware felony gangs have developed a status for not publishing knowledge (or not less than delaying publication) if a ransom is paid.
Extra usually, the encryption, decryption or exfiltration of information is usually a tough and expensive activity for criminals to tug off. It’s far less complicated to delete the information after which declare they’ve been encrypted or exfiltrated and demand a ransom. Nevertheless, if the victims suspect that they received’t be getting the decryption key or encrypted knowledge again then they received’t pay the ransom. And people who do pay a ransom and get nothing in return might disclose that reality. That is more likely to affect the attacker’s “status” and the probability of future ransom funds. Merely put, it pays to play “honest” on the planet of extortion and ransom assaults.
So in lower than ten years we’ve seen the ransomware menace evolve enormously from the comparatively low scale CryptoLocker, to a multi-million greenback enterprise involving organised felony gangs and complicated methods. From 2020 onwards the incidents of ransomware, and consequent losses, have seemingly elevated by one other order of magnitude. Ransomware has turn out to be too large to disregard and is now a serious concern for governments and regulation enforcement.
Crypto extortion threats
Devastating although ransomware has turn out to be, the menace will inevitably evolve additional, as criminals develop new methods for extortion. As talked about already, a key theme in our collective analysis over the past ten years has been to try to preempt the possible methods that criminals can make use of in order to be forward of the sport.
Our analysis is now centered on the subsequent era of ransomware, which we consider will embody variants centered on cryptocurrency, and the “consensus mechanisms” used inside them.
A consensus mechanism is any technique (often algorithmic) used to realize settlement, belief and safety throughout a decentralised laptop community.

Shutterstock/sundaemorning
Particularly, cryptocurrencies are more and more utilizing a so referred to as “proof-of-stake” consensus mechanism, through which traders stake important sums of foreign money, to validate crypto transactions. These stakes are susceptible to extortion by ransomware criminals.
Cryptocurrencies depend on a decentralised blockchain that gives a clear file of all of the transactions which have taken place utilizing that foreign money. The blockchain is maintained by a peer-to-peer community relatively than a government (as with standard foreign money). In precept, the transaction data included within the blockchain are immutable, verifiable and securely distributed throughout the community, giving customers full possession and visibility into the transaction knowledge. These properties of blockchain depend on a safe and non-manipulable “consensus mechanism” through which the unbiased nodes within the community “approve” or “agree” which transactions so as to add to the blockchain.
Till now, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have relied on a so-called “proof-of-work” consensus mechanism through which the authorisation of transactions includes the fixing of advanced mathematical issues (the work). In the long run this strategy is unsustainable as a result of it ends in duplication of effort and avoidable massive scale vitality use.
The choice, which is now turning into a actuality, is a “proof-of-stake” consensus mechanism. Right here, transactions are accredited by validators who’ve staked cash and are financially rewarded for validating transactions. The position of inefficient work is changed by a monetary stake. Whereas this addresses the vitality downside, it implies that massive quantities of staked cash turns into concerned in validating crypto-transactions.
Ethereum
The existence of this staked cash gives a novel menace to some proof-of-stake cryptocurrencies. We’ve got focussed our consideration on Ethereum, a decentralised cryptocurrency that establishes a peer-to-peer community to securely execute and confirm software code, generally known as a sensible contract.
Ethereum is powered by the Ether (ETH) token that enables customers to transact with one another via using these good contracts. The Ethereum challenge was co-founded by Vitalik Buterin in 2013 to beat shortcomings with Bitcoin. On September 15 2022, The Merge, moved the Ethereum community from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, making it one of many first distinguished proof-of-stake cryptocurrencies.
The proof-of-stake consensus mechanism in Ethereum depends on “validators” to approve transactions. To arrange a validator there must be a minimal stake of 32ETH, which is at the moment round US$60,000 (round £43,000). Validators can then earn a monetary return on their stake from working a validator in accordance with Ethereum guidelines. On the time of writing there are round 850,000 validators.
A variety of hope is being pinned on the “stake” answer of validation – however hackers are positive to be trying into how they’ll infiltrate the system.
In our challenge, which was funded by the Ethereum Basis, we recognized methods through which ransomware teams might exploit the brand new proof-of-stake mechanism for extortion.
Slashing
We discovered that attackers might exploit validators via a course of referred to as “slashing”. Whereas validators obtain rewards for obeying the principles, there are monetary penalties for validators which might be seen to behave maliciously. The fundamental goal of penalties is to forestall exploitation of the decentralised blockchain.
There are two types of penalties, probably the most extreme of which is slashing. Slashing happens for actions that ought to not occur accidentally and will jeopardise the blockchain, akin to proposing conflicting blocks are added to the blockchain, or attempting to vary historical past.
Slashing penalties are comparatively extreme with the validator shedding a major share of their stake, not less than 1ETH. Certainly, in probably the most excessive case the validator might lose all of their stake (32ETH). The validator will even be pressured to exit and not act as a validator. Briefly, if a validator is slashed there are large monetary penalties.
To carry out actions, validators are assigned distinctive signing keys, that, in essence, show who they’re to the community. Suppose {that a} felony received maintain of the signing key? Then, they might blackmail the sufferer into paying a ransom.
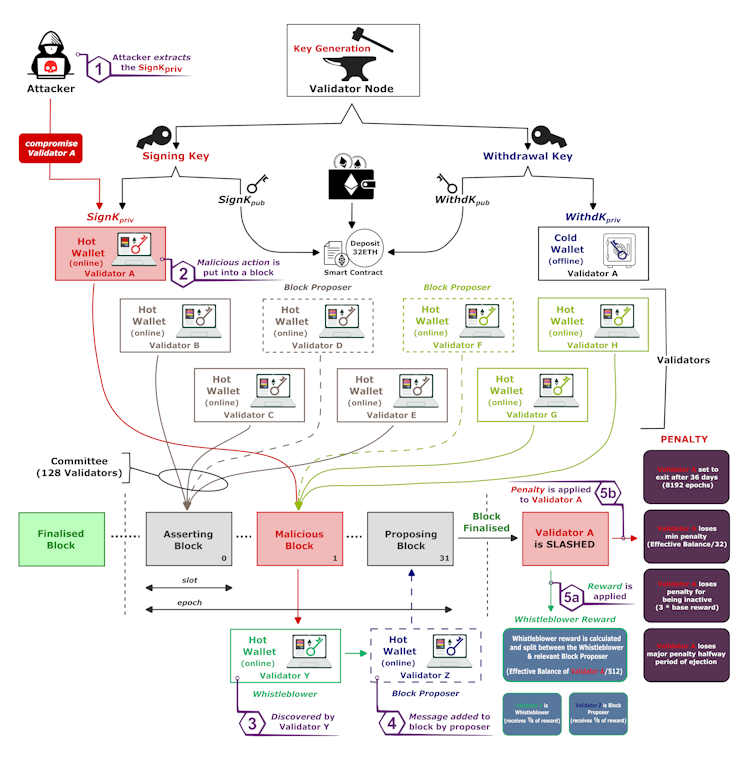
Alpesh Bhudia, CC BY-ND
Move diagram displaying simply how sophisticated it will get when there’s an extortion assault towards proof-of-stake validators, akin to Ethereum
A ‘good contract’
The sufferer could also be reluctant to pay the ransom except there’s a assure that the criminals is not going to take their cash and fail to return/launch the important thing. In spite of everything, what’s to cease the criminals asking for an additional ransom?
One answer we’ve discovered – which harks again to the truth that ransomware has actually turn out to be a form of enterprise operated by criminals who need show they’ve an “trustworthy” status – is a great contract.
This automated contract will be written in order that the method solely works if either side “honour” their facet of the cut price. So, the sufferer might pay the ransom and be assured that it will resolve the direct extortion menace. That is potential via the Ethereum as a result of all of the steps required are publicly observable on the blockchain – the deposit, the signal to exit, the absence of slashing, and the return of the stake.
Functionally, these good contracts are an escrow system through which cash could also be held till pre-agreed situations are met. For example, if the criminals power slashing earlier than the validator has totally exited, then the contract will make sure that the ransom quantity is returned to the sufferer. Such contracts are, nevertheless, open to abuse, and there’s no assure that an attacker-authored contract will be trusted. There may be potential for the contract to be automated in a completely trusted means, however we’ve but to look at such behaviour and techniques emerge.
The staking swimming pools menace
One of these “pay and exit” technique is an efficient means for criminals to extort victims if they’ll receive the validator signing keys.
So how a lot injury would a ransomware assault like this do to Ethereum? If a single validator is compromised then the slashing penalty – and so most ransom demand – can be within the area of 1ETH, which is round US$1,800 (about £1,400). To leverage bigger quantities of cash the criminals, due to this fact, want to focus on organisations or staking swimming pools which might be liable for managing massive numbers of validators.
Keep in mind, that given the excessive entry prices for particular person traders, many of the validating on Ethereum might be run below “staking swimming pools” through which a number of traders can collectively stake cash.
To place this in perspective, Lido is the biggest staking pool in Ethereum with round 127,000 validators and 18% of the whole stake; Coinbase is the second largest with 40,000 validators and 6% of the whole stake. In complete, there are 21 staking swimming pools working greater than a 1,000 validators. Any one in every of these staking swimming pools is liable for tens of thousands and thousands of {dollars} of stake and so viable ransom calls for is also within the thousands and thousands of {dollars}.
Proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms are too younger for us to know whether or not extortion of staking swimming pools will turn out to be an energetic actuality. However the basic lesson of ransomware’s evolution is that the criminals are likely to gravitate in the direction of methods that incentivise cost and improve their illicit beneficial properties.
Probably the most simple means that traders and staking pool operators can mitigate the extortion menace we’ve recognized is by defending their signing keys. If the criminals can not entry the signing keys then there isn’t a menace. If the criminals can solely entry among the keys (for operators with a number of validators) then the menace might fail to be profitable.
So staking swimming pools have to take measures to safe signing keys. This is able to contain a spread of actions together with: partitioning validators so {that a} breach solely impacts a small subset; step up cyber safety to forestall intrusion, and strong inner processes to restrict the insider menace of an worker divulging signing keys.

Shutterstock/Andrii Yalanskyi
The staking pool marketplace for cryptocurrencies like Ethereum is aggressive. There are numerous staking swimming pools, all providing comparatively related providers, and competing on value to draw traders. These aggressive forces, and the necessity to reduce prices, might result in comparatively lax safety measures. Some staking swimming pools might, due to this fact, show a comparatively straightforward goal for criminals.
Finally, this could solely be solved with regulation, better consciousness and for traders in staking swimming pools to demand excessive ranges of safety to guard their stake.
Sadly, the historical past of ransomware suggests that prime profile assaults will must be seen earlier than the menace is taken significantly sufficient. It’s attention-grabbing to ponder the implications of a major breach of a staking pool. The status of the staking pool would presumably be badly affected and so the staking pool’s viability in a aggressive market is questionable. An assault may additionally have implications for the status of the foreign money.
On the most severe, it might result in a foreign money collapsing. When that occurs – because it did with FTX in 2022 following one other hacking assault, there are knock-on results to the worldwide economic system.
Right here to remain
Ransomware might be a problem for years, if not a long time, to return.
One potential imaginative and prescient of the longer term is that ransomware simply turns into a part of regular financial life with organisations going through the fixed menace of assault, with few penalties for the largely nameless gangs of cyber criminals behind the scams.
To preempt such unfavorable penalties we’d like better consciousness of the menace. Then traders could make extra knowledgeable selections over which staking swimming pools and currencies to put money into. It additionally is smart to have a market with many staking swimming pools, relatively than a market dominated by only a few massive ones, as this might insulate the foreign money from potential assaults.
Past crypto, preemption includes funding in cyber safety throughout a spread of kinds – from employees coaching and an organisational tradition that helps reporting of incidents. It additionally includes funding in restoration choices, akin to efficient back-ups, in-house experience, insurance coverage and tried and examined contingency plans.
Sadly, cyber safety practices should not bettering as one may hope in lots of organisations and that is leaving the door open for cyber criminals. Primarily, everybody must get higher at hiding, and defending, their digital keys and delicate info if we’re to face an opportunity towards the subsequent era of ransomware attackers.

For you: extra from our Insights collection:
To listen to about new Insights articles, be a part of the a whole bunch of 1000’s of people that worth The Dialog’s evidence-based information. Subscribe to our publication.
[ad_2]
Source link



