[ad_1]
Why it issues: Firms corresponding to Epic Video games and even the Biden administration have criticized Apple for sustaining a walled backyard and never permitting sideloading in iOS. Nonetheless, one stable purpose for conserving the gates closed is certainly one of Google’s most persistent issues – versioning. Utilizing dynamic code loading, hackers can provide apps vetted by the app retailer with malicious updates by way of a third-party server, and there may be little the shop can do about it.
The Google Cybersecurity Motion Crew (GCAT) notes on this month’s Risk Horizons report that Google Play continues to have a recognized malware drawback. Malicious app builders have been utilizing “versioning” to add malware to seemingly innocuous apps.
First, the risk actor uploads a innocent app to Google Play. The software program incorporates no malware, so it would not set off flags throughout the automated vetting course of. Then the attackers ship malicious updates by way of an owned or compromised server utilizing dynamic code loading (DCL). So the once-safe app turns into a backdoor to the gadget permitting hackers to exfiltrate private info, together with consumer credentials.
“Campaigns utilizing versioning generally goal customers’ credentials, information, and funds.” reads the report. “In an enterprise atmosphere, versioning demonstrates a necessity for defense-in-depth ideas, together with however not restricted to limiting utility set up sources to trusted sources corresponding to Google Play or managing company gadgets by way of a cell gadget administration (MDM) platform.”
Google has recognized concerning the assault vector for some time, however it’s onerous to mitigate for the reason that malicious software program fully bypasses Google Play’s checks. Chances are you’ll recall that a couple of 12 months in the past, the shop purged a number of supposedly protected antivirus apps when safety researchers discovered that the builders had been utilizing DCL to replace the applications with the banking trojan Sharkbot.
Nonetheless, even when Google removes these dangerous apps, extra ultimately spring up, whereas many others stay out there because of sideloading by various app shops. GCAT’s report mentions that Sharkbot stays a typical drawback with Android apps due to DCL. Typically it’s going to discover variations of Sharkbot modified with lowered performance to scale back the possibility of getting ejected by the automated checks. Nonetheless, totally useful editions can run rampant on third-party app shops.
Mitigation in the end falls to the Android end-user or an organization’s IT administrator. Google recommends solely downloading software program from Google Play or different trusted sources. Alternatively, Android Enterprise or third-party Enterprise Mobility Administration options have built-in instruments that enable admins to selectively handle app distribution on firm gadgets. Google moreover suggests leveraging Market allowlists correctly to assist restrict dangers.
[ad_2]
Source link

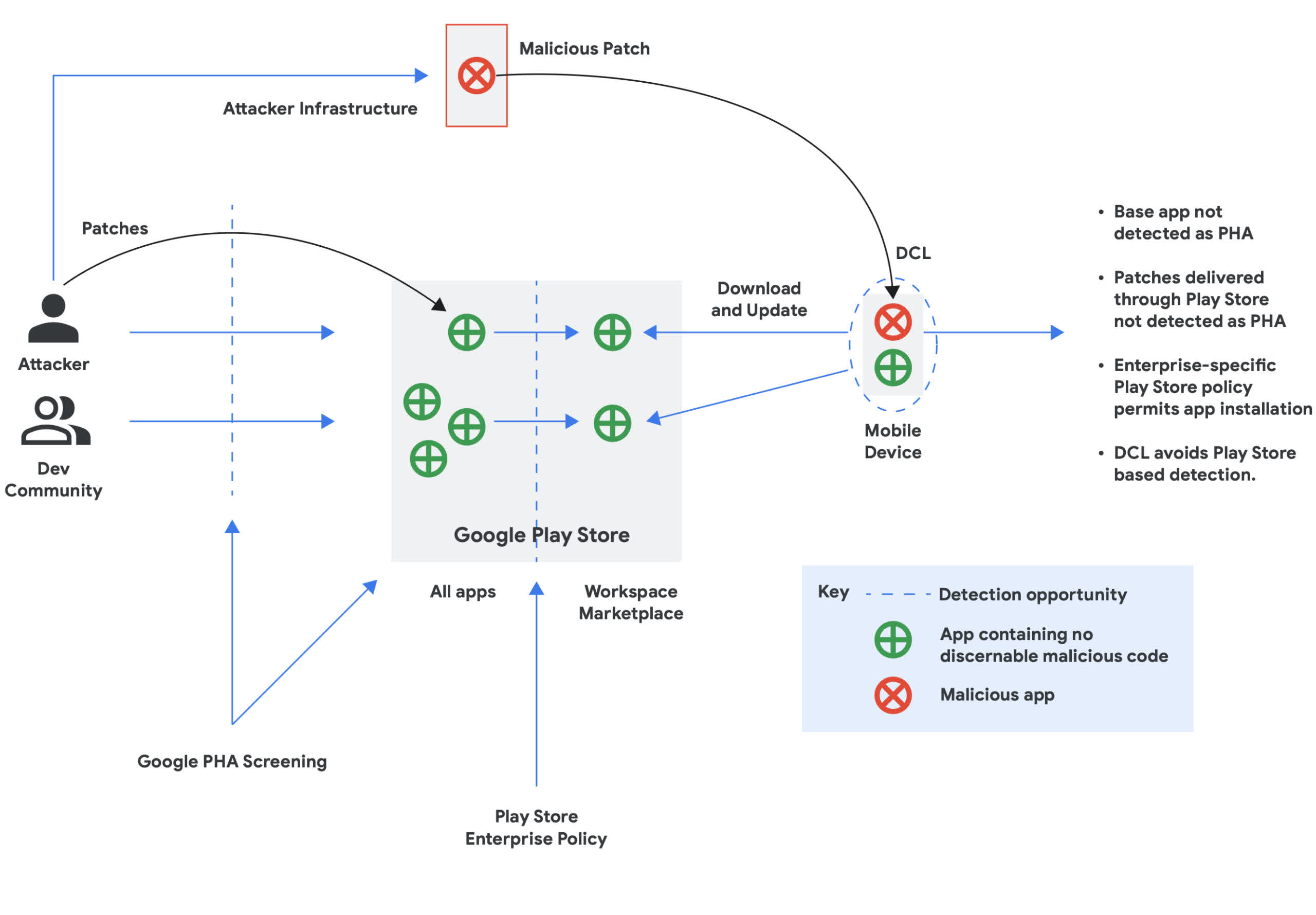 DCL circumvention of Play Retailer based mostly safety controls to patch malicious behaviors into already-installed functions.
DCL circumvention of Play Retailer based mostly safety controls to patch malicious behaviors into already-installed functions.

