[ad_1]
Vegetation vary from easy seaweeds and single-celled pond scum, by way of to mosses, ferns and big timber. Palaeontologists like us have lengthy debated precisely how this numerous vary of sizes and styles emerged, and whether or not crops emerged from algae into multicellular and three-dimensional kinds in a gradual flowering or one large bang.
To reply this query, scientists turned to the fossil file. From these best-preserved examples, like trilobites, ammonites and sea urchins, they’ve invariably concluded {that a} group’s vary of organic designs is achieved through the earliest durations in its evolutionary historical past. In flip, this has led to hypotheses that evolutionary lineages have a better capability for innovation early on and, after this primary part of exuberance, they follow what they know. This even applies to us: all of the totally different placental mammals developed from a standard ancestor surprisingly rapidly. Is identical true of the plant kingdom?
In our new research, we sought to reply this query by in search of sure traits in every main plant group. These traits ranged from the elemental traits of crops – the presence of roots, leaves or flowers – to wonderful particulars that describe the variation and ornamentation of every pollen grain. In complete, we collected information on 548 traits from greater than 400 residing and fossil crops, amounting to greater than 130,000 particular person observations.
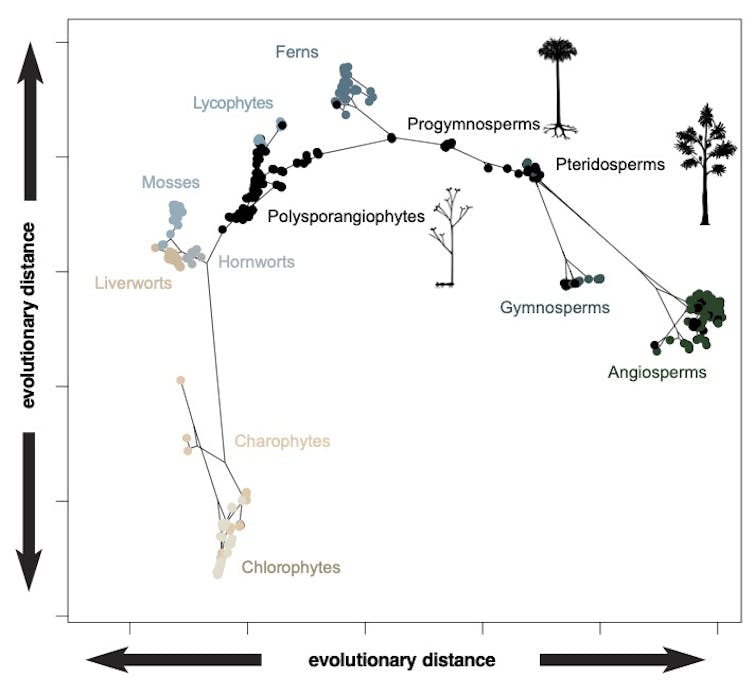
We then analysed all this information, grouping crops primarily based on their general similarities and variations, all plotted inside what could be considered a “design house”. Since we all know the evolutionary relationships between the species, we will additionally predict the traits of their extinct shared ancestors and embody these hypothetical ancestors inside the design house, too.
For instance, we’ll by no means discover fossils of the ancestral flowering plant, however we all know from its closest residing descendants that it was bisexual, radially symmetric, with greater than 5 spirally organized carpels (the ovule-bearing feminine reproductive a part of a flower). Collectively, information factors from residing species, fossils and predicted ancestors reveal how plants has navigated design house by way of evolutionary historical past and over geological time.
Philip Donoghue et al / Nature Vegetation
We anticipated flowering crops to dominate the design house since they make up greater than 80% of plant species, however they don’t. In truth, the residing bryophytes – mosses, liverworts and hornworts – obtain virtually as a lot selection of their physique kinds.
This might not be completely stunning for the reason that three lineages of bryophytes have been doing their very own factor for greater than thrice so long as flowering crops. And regardless of their diminutive nature, even the standard mosses are terribly complicated and numerous when seen by way of a microscope.
The evolutionary relationships conveyed by the branching family tree within the above plot present that there’s, usually, a construction to the occupation of design house – as new teams have emerged, they’ve expanded into new areas. Nonetheless, there may be some proof for convergence, too, with some teams just like the residing gymnosperms (conifers and allies) and flowering crops plotting nearer collectively than they do to their widespread ancestor.
Nonetheless, a few of the distinctiveness of the totally different groupings in design house is clearly the results of extinction. That is clear if we think about the distribution of the fossil species (black dots within the above determine) that always happen between the clusters of residing species (colored dots within the determine).
So how did plant physique plan range evolve?
General, the broad sample is one in every of progressive exploration of recent designs as a results of improvements which can be normally related to copy, just like the embryo, spore, seed and flower. These symbolize the evolutionary options to the environmental challenges confronted by crops of their progressive occupation of more and more dry and difficult niches on the land floor. For instance, the innovation of seeds allowed the crops that bear them to breed even within the absence of water.

ANGHI / shutterstock
Over geological time, these expansions happen as episodic pulses, related to the emergence of those reproductive improvements. The drivers of plant anatomical evolution seem like a mixture of genomic potential and environmental alternative.
Plant disparity means that the large bang is a bust
None of this matches with the expectation that evolutionary lineages begin out modern earlier than turning into exhausted. As a substitute, it appears elementary types of crops have emerged hierarchically by way of evolutionary historical past, elaborating on the anatomical chassis inherited from their ancestors. They haven’t misplaced their capability for innovation over the billion or extra years of their evolutionary longevity.
So does that make crops totally different from animals, research of that are the idea for the expectation of early evolutionary innovation and exhaustion? Under no circumstances. Comparable research that we’ve got accomplished on animals and fungi present that, while you research these multicellular kingdoms of their entirety, all of them exhibit a sample of episodically growing anatomically selection. Particular person lineages could quickly exhaust themselves however, general, the kingdoms carry on innovating.
This means a normal sample for evolutionary innovation in multicellular kingdoms and in addition that animals, fungi and crops nonetheless have loads of evolutionary juice of their tanks. Let’s hope we’re nonetheless round to see what innovation arises subsequent.
[ad_2]
Source link



