[ad_1]
The most recent UK shopper worth index (CPI) knowledge has been hailed as a win for prime minister Rishi Sunak’s intention to half inflation, introduced earlier this yr. Costs rose by 4.6% in October 2023, bringing the speed of worth development right down to its lowest level since an October 2022 peak of 11.1%.
However inflation coming down regularly doesn’t imply costs are falling – they’re merely growing at a slower tempo. Costs stay excessive, deepening the price of dwelling disaster for a lot of, particularly these whose nominal wages haven’t elevated at tempo with inflation in recent times.
Compounding this, poor households spend a much bigger proportion of their revenue on meals, power, and hire – three prices which have spiked essentially the most in recent times, and nonetheless stay excessive.
A decline in power costs was the most important contributor to the latest inflation slowdown. However though electrical energy, gasoline and different gas prices have fallen by 21.7% since October 2022, these costs stay very excessive.
Gasoline costs are about 60% greater than they had been in October 2021 and the worth of electrical energy is about 40% greater. In comparison with January 2021, electrical energy, gasoline and different gas prices are at the moment 82% greater.
Annual inflation within the worth of meals and non-alcoholic drinks can be nonetheless excessive at 10.1%. October 2023 meals costs had been round 30% greater than in October 2021, whereas personal rents are up by 11.5% in comparison with January 2021.
The federal government’s fears of a wage-price spiral – its reasoning for holding out towards public sector strikes for therefore lengthy – have additionally didn’t materialise.
An ample enhance in public sector pay in well being, training and the civil service would have reversed a long time of below-inflation pay for these employees. And public sector wages don’t immediately result in rising enter prices for personal corporations, and so would have completed little to gas a wage-price spiral.
À lire aussi :
Strikes: why refusing public sector pay rises will not assist cut back inflation
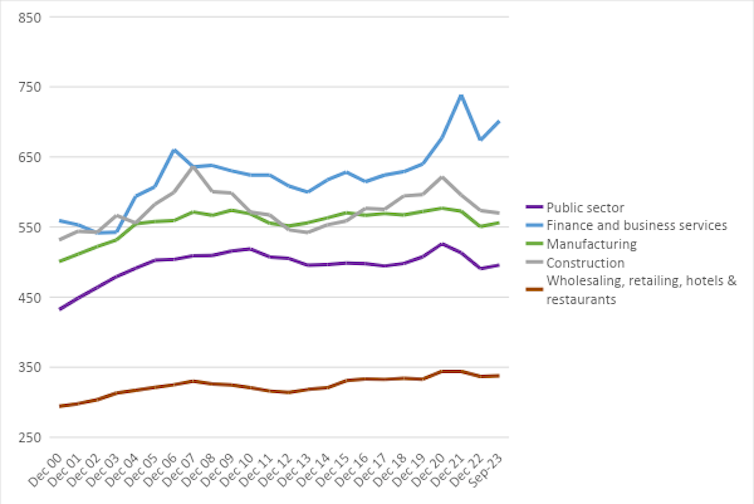
Current wage disputes and excessive job emptiness charges have delivered solely modest will increase in actual pay within the public sector (1.4%). Wages have stagnated in manufacturing and wholesaling, retailing, accommodations and eating places sectors, and fallen in building (by 2.8%) as of September 2023 in comparison with September 2022.
The one sectors that noticed a considerable actual pay rise are finance and enterprise providers (2%) and transport and storage (15.8%). In actual fact, actual wages stay under pre-pandemic ranges in all different sectors.
Wages are stagnant or falling in some sectors:
Writer supplied utilizing Workplace for Nationwide Statistics knowledge., CC BY-NC-ND
Boosting earnings
In the meantime, some corporations have added the rising prices of inputs like power and meals into the worth of the products they promote, squeezing the poorly-paid from the opposite aspect. Some have even elevated their revenue margins since 2021 by elevating costs at a sooner charge than the rise of their enter prices.
A Financial institution of England survey reveals most of the corporations with the best revenue margins are anticipated to extend their revenue margins additional in 2023, whereas corporations with the bottom revenue margins reported a drop in 2022, and are solely anticipated to see a partial restoration this yr.
Wages may enhance with out inflicting greater inflation if the highest corporations minimize their revenue margins. This could additionally assist the corporations who weren’t in a position to move on excessive enter, wages or borrowing prices to their prospects. With firm insolvencies at a 14-year excessive, they’re as a substitute slicing again non-essential spending.
However the authorities has completed little to handle the rise in revenue margins for the highest corporations past a restricted power worth cap and windfall taxes on power corporations. As meals costs soared, authorities intervention amounted to conferences with the farmers, meals producers and a few of Britain’s largest supermarkets to debate capping worth will increase in 2023 with out precise worth controls.
À lire aussi :
Six methods the upcoming autumn assertion may have an effect on your private funds
Chancellor Jeremy Hunt’s upcoming autumn assertion is unlikely to supply many strong options to deal with the price of dwelling disaster or issues with public bodily and social infrastructure. Hunt is predicted to stay to the narrative {that a} discount in public debt/GDP is important to struggle inflation.
Equally, the Financial institution of England could maintain rates of interest once more at its subsequent Financial Coverage Committee assembly in December, regardless of stagnation in shopper demand and enterprise funding.
These insurance policies is not going to assist to handle the a number of intersecting crises going through the UK proper now, together with inequalities at school, gender and race, ecological breakdown, geopolitical turmoil and technological change – to not point out the continued value of dwelling disaster.
[ad_2]
Source link



